Lyrid Meteor Shower - 2019
- Details
- Written by AndEl

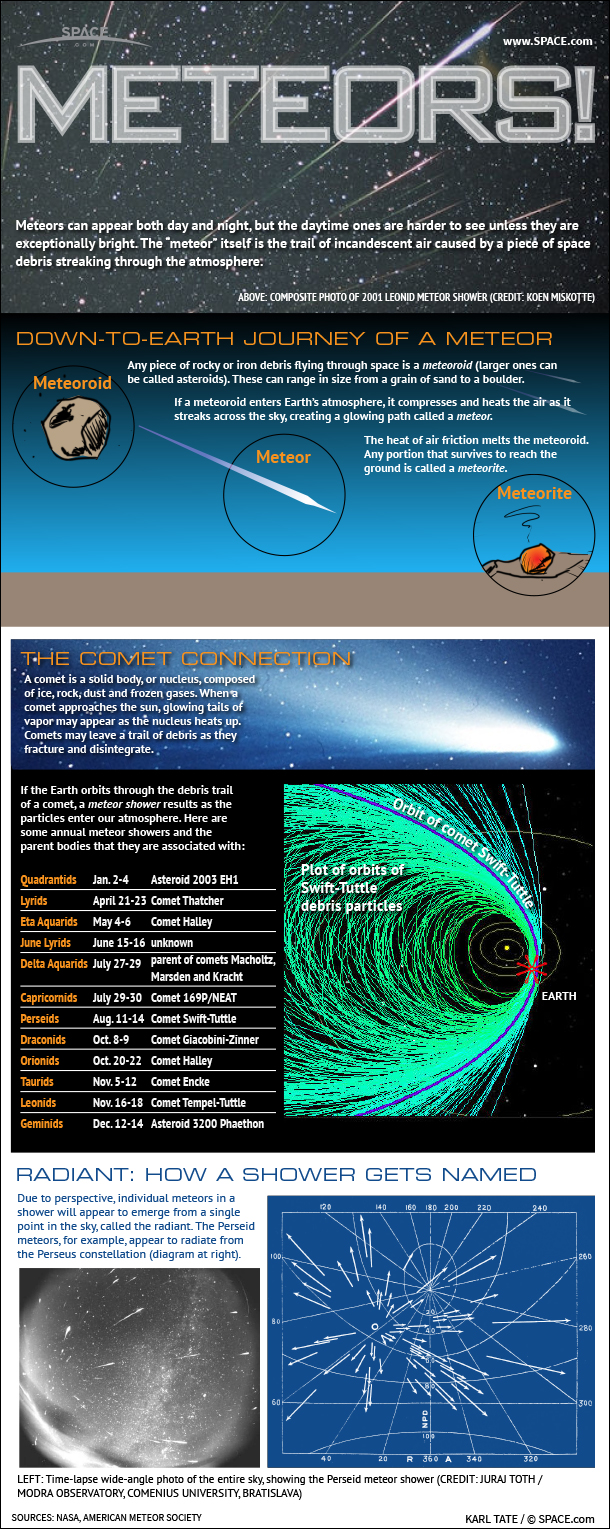
In late April, skywatchers in the Northern Hemisphere will get a view of the Lyrid meteor shower, the dusty trail of a comet with a centuries-long orbit around the sun. The Lyrid meteors streak across the sky between April 16 and April 25, so skywatchers have a chance to see them during that window, weather permitting.
The best day to see Lyrid meteors will be extremely early in the morning on Monday, April 22, NASA meteor expert Bill Cooke told Space.com. As with most meteor showers, the peak viewing time will be before dawn. A waning gibbous moon (very close to full) will wash out all but the very brightest meteors this year during the peak, however.
Cooke said the average Lyrid shower produces 15 to 20 meteors per hour; this year, the meteor shower should hit about 18 per hour. Some years, the Lyrid meteor shower intensifies and can produce up to 100 meteors per hour in what's called an "outburst," but it is difficult to predict exactly when that will happen.
"People say there is some periodicity there," Cooke said, "but the data doesn't support that." Although there is an average of 30 years between these outbursts, that's only an average; the actual number of years between the events varies, Cooke said.
Where to look
The radiant — the point from which the meteors appear to originate — will be high in the evening sky in the constellation Lyra to the northeast of Vega, one of the brightest stars visible in the night sky this time of year. Don't look directly toward the radiant, though, because you might miss the meteors with the longest tails.
"The moon will be really favorable for them this year; it will set by the time the Lyrid radiant is high in the sky," Cooke told Space.com. "The moon will be around first quarter, so the moon will have set by the show getting fired up after midnight."
The Lyrid meteor shower is of medium brightness, but not as luminous as the famous Perseid meteor shower in August, which tends to produce more prominent trails, Cooke said.
What causes the Lyrids?
Lyrid meteors are little pieces of Comet Thatcher, a long-period comet that orbits the sun about once every 415 years. Pieces of debris left in the comet's wake, however, make an appearance every year. (Comet Thatcher's most recent perihelion, or closest approach to the sun, was in 1861. It won't be back until the year 2276.)
Meteor showers occur when the Earth crosses the path of a comet, colliding with a trail of comet crumbs. That's why they happen around the same time every year and appear to originate from specific points in the sky. As they burn up in the atmosphere, the meteors leave bright streaks in the sky commonly referred to as "shooting stars." [Infographic: How Meteor Showers Work]
Lyrid meteors come in fast — though not as fast as the Leonids, which peak in November, Cooke said. "The Leonids hit us head-on," he said. "The Lyrids are more like hitting the left front fender."
The Lyrids are one of the oldest recorded showers, Cooke said, with observations going back to 687 B.C. You don't need any kind of special equipment to see the meteors; just look up at the dark sky, be patient and enjoy the show.
Liked this article? Dive deeper into personal growth and wellness! Check out CrystalWind.ca for spiritual wisdom or explore AromaWorx.ca for natural well-being tips. Spread the positivity—share this with friends on their happiness journey!
Let’s Chat! Drop Your Thoughts Below! ![]()
Latest Articles
Dive into the Mystical World of the Crystal Wind Oracle Deck!
Get All the Enchanting Details Now!
NEW Expanded Boxed Edition!
Now with 58 Cards for Richer Wisdom!

Imagine a world of inspiration and healing, free for all—made possible by YOU!
Donate Now—Ignite the Magic at CrystalWind.ca!

Epilepsy - Finding A Cure
Your donation can make a difference!
Help us find a cure – donate now!
Unlock Your Light: Join Lightworkers Worldwide on CrystalWind.ca!
Articles: The Founders
Articles: Cosmic Neighbours
Articles: Galactic History
Follow Us!
Featured This Month
Chalcedony
The Stone Of Orators Chalcedony was very popular as a decorative stone in ant... Read more
Abalone Shell
Echos Of The Ancestors Abalone strengthens the structure of the body and th... Read more
Lammas by The Hedgewitch
Although in the heat of a Mid-western summer it might be difficult to discer... Read more
Lugh - Celtic God Of The Sun
The god Lugh was worshiped in Ireland as a deity of the sun. This connection... Read more
Egyptian Zodiac/Astrology
Egyptian astrology was one of the earliest forms of astrology. The Egyptians w... Read more
Sun in Cancer
Cancer Sun Sign Characteristics Overview The name "Cancer" comes from Latin, ... Read more
Cancer Mythology
The Mythology of Cancer: A Celestial Tale of Loyalty and Sacrifice Among th... Read more