Quadrantid Meteor Shower - 2020
- Details
- Written by AndEl

The Quadrantid meteor shower is 2020’s first major meteor shower. We’ll have moon-free skies during the predawn hours on January 4 for this year’s peak, expected late night January 3 until dawn January 4. Although the Quadrantids have been known to produce some 50-100 meteors in a dark sky, their peak is extremely narrow, time-wise. Peaks of the Perseid or Geminid meteor showers persist for a day or more, allowing all time zones around the world to enjoy a good display of Perseids or Geminids. But the Quadrantids’ peak lasts only a few hours.
So you have to be on the right part of Earth – preferably with the radiant high in your sky – in order to experience the peak of the Quadrantids. What’s more, the shower favors the Northern Hemisphere because its radiant point is so far north on the sky’s dome.
So you need some luck to see the Quadrantids, and being in the Northern Hemisphere does help. Who will see the 2020 shower? Keep in mind the prediction of the Quadrantid peak represents an educated guess, not an ironclad guarantee.
That said, in 2020 the International Meteor Organization gives the peak as January 4 at 08:00 UTC. If that prediction of the peak holds true, North America has a good shot at viewing the shower at its best during the predawn hours on January 4.
Just know that meteor showers are notorious for defying the best-laid forecasts. Thus for the Quadrantids – as for any meteor shower – your best plan is simply to look for yourself.
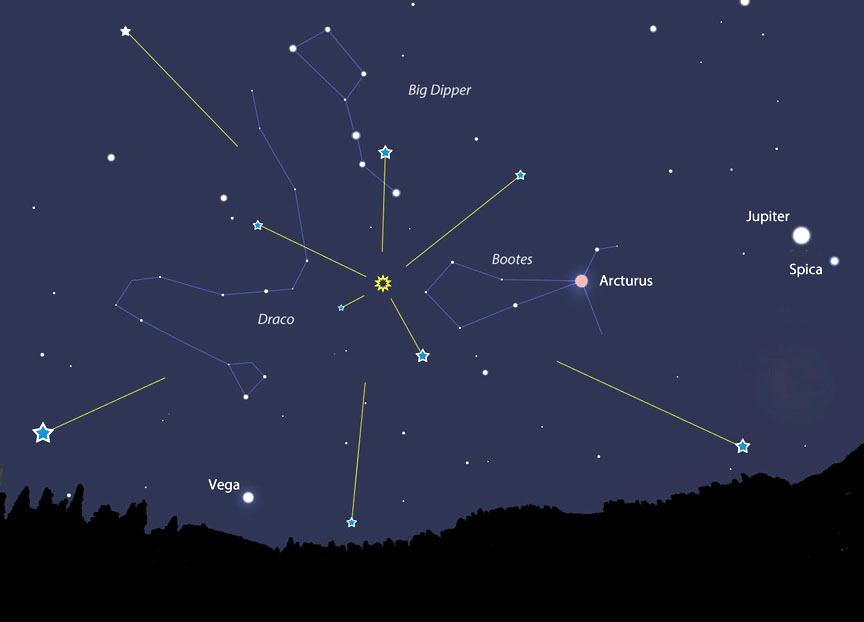
To find the radiant, you will need to look for the constellation Bootes. The easiest way to find it is to look north for the Big Dipper. Then, follow the "arc" of the Big Dipper's handle across the sky to the red giant star Arcturus, which anchors the bottom of Bootes.
If you happen to catch the shower at an off-peak moment, rates of about 25 meteors per hour are still expected. In the past, Lunsford has recommended keeping Bootes in your field of view, but looking slightly away so that you catch the meteors with the longer tails.
Where do they come from?
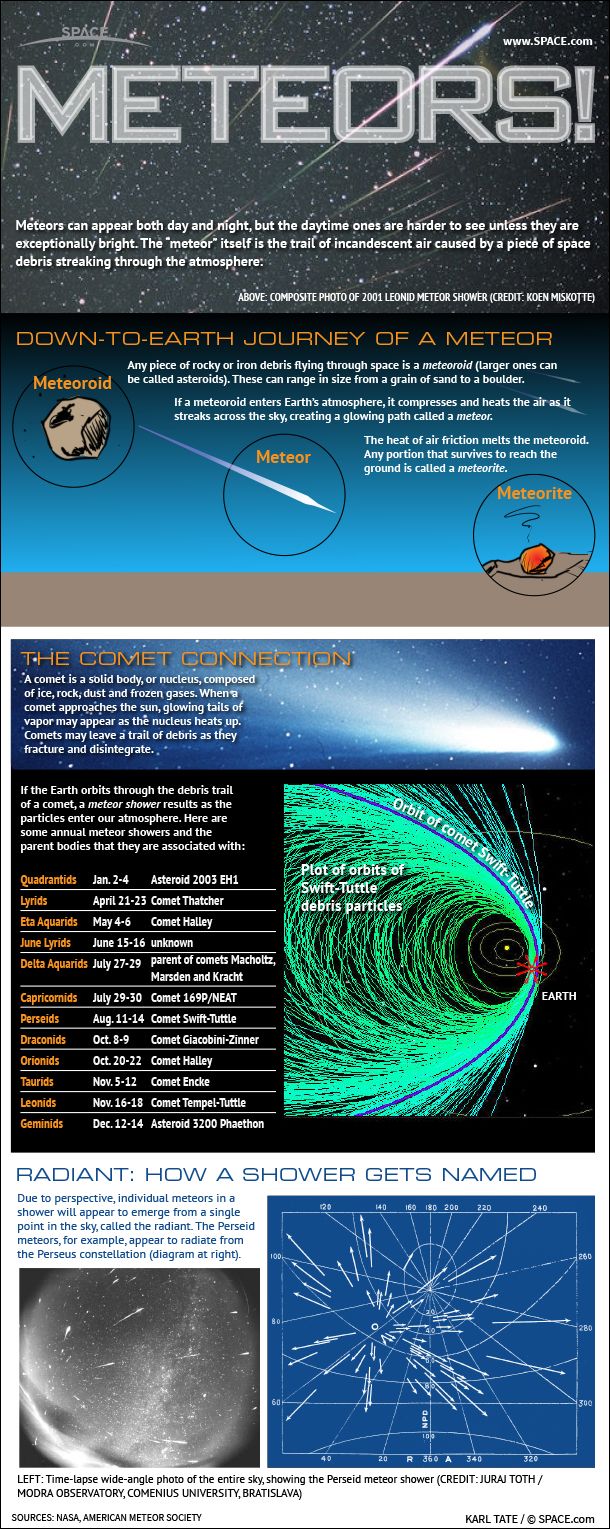
The Quadrantids are thought to be associated with asteroid 2003 EH1, which is likely an extinct comet, Cooke has told Space.com. "It was either a piece of a comet or a comet itself, and then it became extinct," which means that all the ice and other volatiles on the comet have evaporated, he said.
The asteroid has a perihelion (closest approach to the sun) just inside the Earth's orbit, which is pretty far away in celestial terms. Scientists also think that the asteroid may have some connection to the Comet 96P/Machholtz, a comet that orbits the sun once every six years. First observations of the Quadrantids shower appear to be in Europe in the 1820s and 1830s. [How Meteor Showers Work (Infographic)]
How to get the best view
Binoculars and telescopes are not useful for meteor showers; your eyes are enough to see the shooting stars streaking overhead. Find a dark sky and give your eyes about 20-30 minutes to adjust.
Dress warmly and face a little away from the radiant in Bootes to catch the longer-streaking meteors.
© 2020 crystalwind.ca. All rights reserved.
Liked this article? Dive deeper into personal growth and wellness! Check out CrystalWind.ca for spiritual wisdom or explore AromaWorx.ca for natural well-being tips. Spread the positivity—share this with friends on their happiness journey!
Let’s Chat! Drop Your Thoughts Below! ![]()
Latest Articles
Dive into the Mystical World of the Crystal Wind Oracle Deck!
Get All the Enchanting Details Now!
NEW Expanded Boxed Edition!
Now with 58 Cards for Richer Wisdom!

Imagine a world of inspiration and healing, free for all—made possible by YOU!
Donate Now—Ignite the Magic at CrystalWind.ca!

Epilepsy - Finding A Cure
Your donation can make a difference!
Help us find a cure – donate now!
Unlock Your Light: Join Lightworkers Worldwide on CrystalWind.ca!
Articles: The Founders
Articles: Cosmic Neighbours
Articles: Galactic History
Follow Us!
Featured This Month
Mabon Magic: Ideas For Fall Decoration And R…
Welcome (almost!) to Fall! We’re turning the Great Wheel once again, toward ... Read more
Mabon in Modern Times: Fresh Takes on the Au…
The Mabon season begins somewhere around the 21st-22nd of September and cont... Read more
The Vine: September 2nd - September 29th
The Autumnal Equinox ( Alban Elfed ) Celtic Symbol : The White Swan Read more
Watermelon Tourmaline
Synonym: Rainbow Tourmaline The watermelon tourmaline is a rare variety t... Read more
Virgo Mythology
The Virgo Myth In all of constellation mythology, few legends are as misund... Read more
Peridot: The Healer's Stone
Peridot has been used as a Power Stone for centuries. Peridot fosters emotio... Read more
Sweet Violet
Sweet Violet Faithfulness and modesty. “I will always be true to you.” Helps... Read more
Sun in Virgo
An Overview of Sun Sign Characteristics for Virgo Virgo is guided by Mercur... Read more
Crystals for Virgo
As the warmth of summer begins to soften into the crispness of autumn, the Sun... Read more