Orionid Meteor Shower - 2018
- Details
- Written by And-El
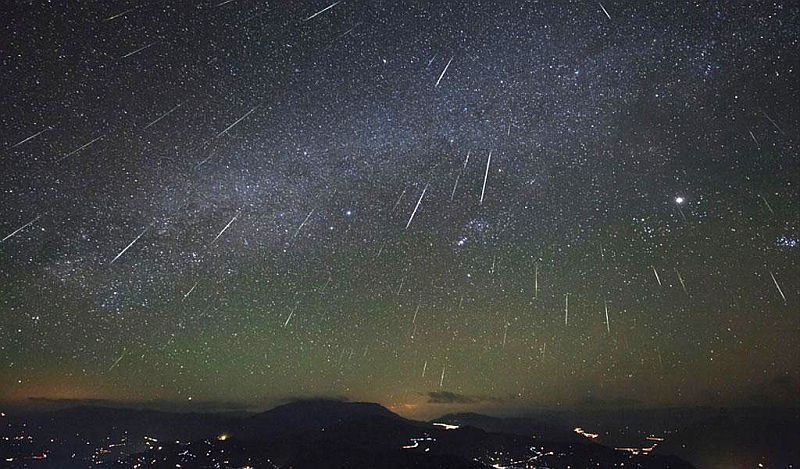

The Orionid meteor shower is set to peak the night of Oct. 21-22, but the moon will lead to subpar views for this night sky display. The meteors that streak across the sky are some of the fastest among meteor showers, because the Earth is hitting a stream of particles almost head on.
"The moon is going to mess with you," NASA meteor expert Bill Cooke told Space.com, and 15-20 meteors per hour should be visible.
The particles come from Comet 1P/Halley, better known as Halley's Comet. This famous comet swings by Earth every 75 to 76 years, and as the icy comet makes its way around the sun, it leaves behind a trail of comet crumbs. At certain times of the year, Earth's orbit around the sun crosses paths with the debris.
"You can see pieces of Halley's Comet during the Eta Aquarids [in May] and the Orionid meteor shower [in October and November]," Cooke told Space.com.
Orionid Meteor Shower: Leftovers of Halley's Comet
The Orionids are named after the direction from which they appear to radiate, which is near the constellation Orion (The Hunter). In October, Orion is best visible around 2 a.m. Cooke told Space.com that the best viewing will be around that time on Oct. 21 and Oct. 22. If you miss the peak, the show is also visible between Oct. 15 and 29, as long as the moon isn't washing the meteors out.
Sometimes the shower peaks at 80 meteors an hour; at others it is closer to 20 or 30. Cooke predicted that in 2018, the peak would be at the smaller end of the scale, echoing the peaks of 2017 and years before.
How to view the show
Orionid meteors are visible from anywhere on Earth and can be seen anywhere across the sky. If you find the shape of Orion the Hunter, the meteor shower's radiant (or point of origin) will be near Orion's sword, slightly north of his left shoulder (the star Betelgeuse). But don't stare straight at this spot, Cooke said, "because meteors close to the radiant have short trails and are harder to see — so you want to look away from Orion."
As is the case with most nighttime skywatching events, light pollution can hinder your view of the Orionid meteor shower (although this year, the moon will do damage as well). If possible, get far away from city lights, which can hinder the show. Go out around 1:30 a.m. and let your eyes adjust to the dark for about 20 minutes. Bundle up against the cold if necessary. Lie back and use only your eyes to watch the sky. Binoculars and telescopes won't improve the view, because they are designed to see more stationary objects in the sky
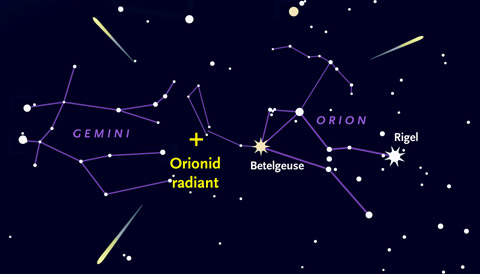
Orionid meteors are visible from anywhere on Earth and can be seen anywhere across the sky. If you find the shape of Orion the Hunter, the meteor shower's radiant (or point of origin) will be near Orion's sword, slightly north of his left shoulder (the star Betelgeuse). But don't stare straight at this spot, Cooke said, "because meteors close to the radiant have short trails and are harder to see — so you want to look away from Orion."
As is the case with most nighttime skywatching events, light pollution can hinder your view of the Orionid meteor shower. If possible, get far away from city lights (which can hinder the show). Go out around 1:30 a.m. and let your eyes adjust to the dark for about 20 minutes. Bundle up against the cold if necessary. Lie back and use only your eyes to watch the sky. Binoculars and telescopes won't improve the view, because they are designed to see more stationary objects in the sky.
Some Orionids will appear very fast and bright, since they can whiz by at up to 148,000 mph (238,000 km/h) in relative speed. That's just six kilometers an hour slower than the Leonids, the speediest show of the year, Cooke said.
It's tempting to think that the brighter meteors represent fragments that would reach the ground, but Cooke said that isn't the case with the Orionids. These tiny comet fragments — some as small as a grain of sand — are called meteoroids. When they enter Earth's atmosphere, they become meteors. Friction from air resistance causes meteors to heat up, creating a bright, fiery trail commonly referred to as a shooting star. Most meteors disintegrate before making it to the ground. The few that do strike the Earth's surface are called meteorites. [How Often Do Meteorites Hit the Earth?]
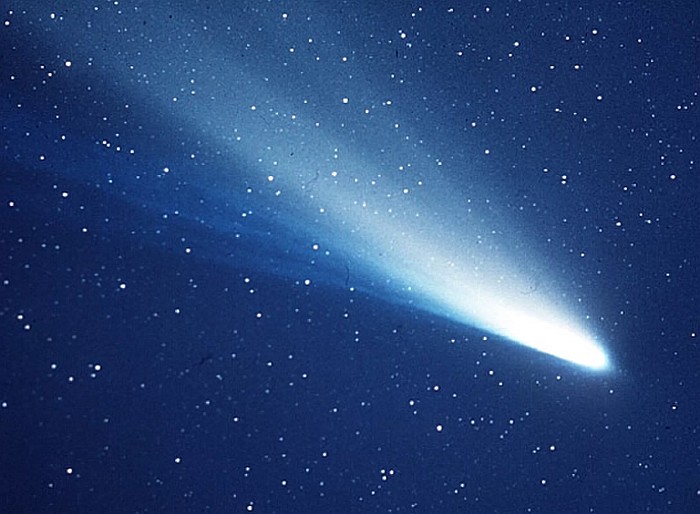

Cometary origins
Astronomers have recorded Halley's Comet as far back as 240 B.C. but no one realized that the same comet was making multiple appearances. In 1705, then-University of Oxford professor and astronomer Edmund Halley published "Synopsis Astronomia Cometicae" ("A Synopsis of the Astronomy of Comets"), which showed the first evidence that the comet is reoccurring. By studying the historical records of a comet that appeared in 1456, 1531, 1607 and 1682, Halley calculated that it was in fact the same comet and predicted it would reappear in 1758. While Halley died before the comet's return, it did appear on schedule and was named after him.
Reports of the Orionids, however, did not first appear until 1839 when an American in Connecticut spotted the shower, Cooke said. More observations of the shower were recorded during the Civil War between 1861 and 1865. Cooke told Space.com he wasn't sure why the meteor shower was discovered so late, given that records of Halley's Comet exist for millennia.
The next perihelion (closet approach of Halley's Comet to the sun) is expected around July 2061.
FROM NASA - UPDATE 
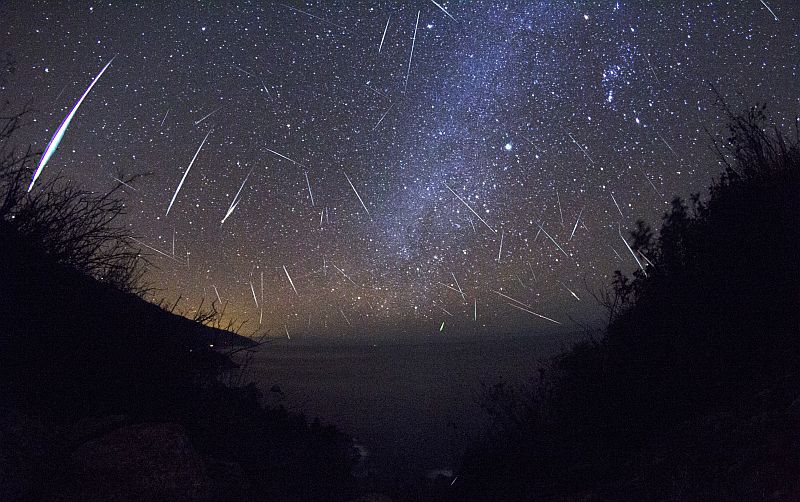

Orionid meteors appear every year around this time when Earth travels through an area of space littered with debris from Halley’s Comet. This year the peak will occur on the night of Wednesday, Oct. 21 into the morning of Thursday, Oct. 22.
“The Orionids will probably show weak activity this year,” says Bill Cooke of the NASA Meteoroid Environments Office . “Bits of comet dust hitting the atmosphere will probably give us about a dozen meteors per hour.”
The best time to look for Orionid meteors is just before sunrise on Thursday, October 22nd, when Earth encounters the densest part of Halley’s debris stream.
Observing is easy: Wake up a few hours before dawn, go outside and look up. No telescope is necessary to see Orionids shooting across the sky. Viewing conditions are favorable this year, as the light from the gibbous Moon should set by 2 a.m. EDT time, permitting good viewing just before dawn when the rates will be at their highest.
A live stream of the night sky from NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. will be available via Ustream beginning October 21, at 10 p.m. EDT. The live feed is an alternative for stargazers experiencing bad weather or light-polluted night skies. If the weather in Huntsville is clear, Orionids may be seen in the feed as early as 11:30 p.m. EDT, though the hours before dawn should show the most Orionid activity.
The display will be framed by some of the prettiest stars in the night sky. In addition to Orionids, you’ll see the Dog Star Sirius, bright winter constellations such as Orion, Gemini, and Taurus, and the planets Jupiter and Venus. Even if the shower is a dud, the rest of the sky is dynamite.
Set your alarm, brew some hot chocolate and enjoy the show!
Liked this article? Dive deeper into personal growth and wellness! Check out CrystalWind.ca for spiritual wisdom or explore AromaWorx.ca for natural well-being tips. Spread the positivity—share this with friends on their happiness journey!
Let’s Chat! Drop Your Thoughts Below! ![]()
Latest Articles
Dive into the Mystical World of the Crystal Wind Oracle Deck!
Get All the Enchanting Details Now!
NEW Expanded Boxed Edition!
Now with 58 Cards for Richer Wisdom!

Imagine a world of inspiration and healing, free for all—made possible by YOU!
Donate Now—Ignite the Magic at CrystalWind.ca!

Epilepsy - Finding A Cure
Your donation can make a difference!
Help us find a cure – donate now!
Unlock Your Light: Join Lightworkers Worldwide on CrystalWind.ca!
Articles: The Founders
Articles: Cosmic Neighbours
Articles: Galactic History
Follow Us!
Featured This Month
Crystals for Virgo
As the warmth of summer begins to soften into the crispness of autumn, the Sun... Read more
Virgo Mythology
The Virgo Myth In all of constellation mythology, few legends are as misund... Read more
Watermelon Tourmaline
Synonym: Rainbow Tourmaline The watermelon tourmaline is a rare variety t... Read more
Peridot: The Healer's Stone
Peridot has been used as a Power Stone for centuries. Peridot fosters emotio... Read more
Sweet Violet
Sweet Violet Faithfulness and modesty. “I will always be true to you.” Helps... Read more
Mabon in Modern Times: Fresh Takes on the Au…
The Mabon season begins somewhere around the 21st-22nd of September and cont... Read more
Mabon Magic: Ideas For Fall Decoration And R…
Welcome (almost!) to Fall! We’re turning the Great Wheel once again, toward ... Read more
Sun in Virgo
An Overview of Sun Sign Characteristics for Virgo Virgo is guided by Mercur... Read more
The Vine: September 2nd - September 29th
The Autumnal Equinox ( Alban Elfed ) Celtic Symbol : The White Swan Read more