Anubis
- Details
- Written by AndEl

Anubis
by Stephanie Cass
Anubis, who the ancient Egyptians called Ienpw (phonetically "Yinepu"), is the mysterious canid funerary deity of ancient Egypt. Even the meaning of his name is unknown -- speculations range from "Royal Child" to having derived from the world for "to putrefy". Both certainly fit the deity, who was at various points in time of Egyptian history known as the lord of the dead before Osiris and, later, became popularly known as the son of Osiris.
Just what type of animal Anubis is represented by is unknown as well; definitely canid and most likely a jackal or a wild dog -- or a hybrid of both -- but, as in the case of Seth, with alterations that deliberately smudge the lines of reality. The deep black color Anubis's animal is not reflective of its actual coat but is instead symbolic of his position as a funerary deity. The reason for Anubis's animal being canid is based on what the ancient Egyptians themselves observed of the creature -- dogs and jackals often haunted the edges of the desert, especially the cemeteries where the dead were buried.
Anubis is an extremely ancient deity. The oldest mastabas of the Old Kingdom have prayers to him carved into their walls, and he is mentioned in the Pyramid Texts in his most celebrated role as a guardian and protector of the dead. A standard offering formula for the dead in the Old Kingdom began thusly:
"An offering which the king gives and Anubis, who is upon his mountain and in the place of embalming, the lord of the necropolis...."
 As mentioned previously, Anubis began in the position that Osiris would later command. In the earliest period of Egyptian religion Anubis was clearly the lord of the dead and Osiris the embalmed god while Anubis performed the act of embalming. Titles that were invested unto Osiris -- such as Khenty-Imentiu or "Foremost of Westerners" -- were originally Anubis's. As the drama of Osiris's death and vindication unfolded over the centuries, Anubis assumed the role of the guide who holds steady the scales on which their hearts are measured against the feather of ma'at as "He Who Counts the Hearts". Should the heart be light as the feather, the soul would then be lead by Anubis (or, in some cases, Harseisis) to be presented to Osiris. Should the heart be heavy, it is fed to Ammit and the soul destroyed.
As mentioned previously, Anubis began in the position that Osiris would later command. In the earliest period of Egyptian religion Anubis was clearly the lord of the dead and Osiris the embalmed god while Anubis performed the act of embalming. Titles that were invested unto Osiris -- such as Khenty-Imentiu or "Foremost of Westerners" -- were originally Anubis's. As the drama of Osiris's death and vindication unfolded over the centuries, Anubis assumed the role of the guide who holds steady the scales on which their hearts are measured against the feather of ma'at as "He Who Counts the Hearts". Should the heart be light as the feather, the soul would then be lead by Anubis (or, in some cases, Harseisis) to be presented to Osiris. Should the heart be heavy, it is fed to Ammit and the soul destroyed.
As Imy-ut, or "He Who is In the Place of Embalming", Anubis is the embalmer who washes the entrails of the dead and guards over their physical bodies as well as the places that house them (the tomb and the necropolis). Priests wearing a mask of Anubis were responsible for the Opening of the Mouth ceremony that reawakened a dead person's senses. In a reflection of the royal seal used on the tombs of the Valley of the Kings depicting pharaoh's victory over the "nine bows" (enemies of Egypt), Anubis is shown recumbent over nine bows meant to be hostile forces of the Underworld who he -- as "Jackal Ruler of the Bows" -- has triumphed over.
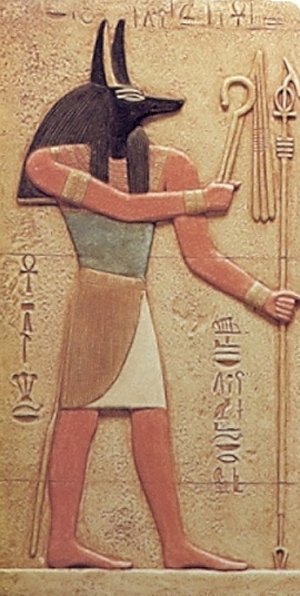
Anubis's parentage is a mystery -- in one tradition he is the son of Nebt-het (Nephthys) and Ra. In yet another, from the Coffin Text period, the cow goddess Hesat is his mother and, from the same source, Bastet is even accounted as his mother (most likely a pun on the ointment jars that comprise her hieroglyphs -- the same jars that were used during the embalming process Anubis was lord of). The Pyramid Texts even supply Anubis with a daughter in the form of the goddess Qeb-hwt ("Cooling Water") -- a celestial serpent or ostrich Who purifies and quenches the monarch.
Anubis is depicted most often as a man with the head of a black canid with alert, pointed ears. He is also represented by a full black canid wearing ribbons and holding a flagellum in the crook of its arm. Very rarely is he ever shown fully human, though there are some cases (such as in the temple of Ramesses II of Abydos) of this. Perhaps the most famous representation of Anubis, the gold-gilded wooden canid found in the tomb of Tutankhamen, was doubtlessly placed there as a protector of the dead and guardian of the tomb.
Anubis was worshipped throughout Egypt, but the center of his cult was in Cynopolis (Upper Egypt).
 The name of Anubis in hieroglyphs.
The name of Anubis in hieroglyphs.
"Anubis." Encyclopedia Mythica from Encyclopedia Mythica Online.
<http://www.pantheon.org/articles/a/anubis.html>
[Accessed October 27, 2009].
Liked this article? Dive deeper into personal growth and wellness! Check out CrystalWind.ca for spiritual wisdom or explore AromaWorx.ca for natural well-being tips. Spread the positivity—share this with friends on their happiness journey!
Let’s Chat! Drop Your Thoughts Below! ![]()
Latest Articles
Articles: Emerald Tablets
Articles: Feng Shui

Imagine a world of inspiration and healing, free for all—made possible by YOU!
Donate Now—Ignite the Magic at CrystalWind.ca!

Epilepsy - Finding A Cure
Your donation can make a difference!
Help us find a cure – donate now!
Unlock Your Light: Join Lightworkers Worldwide on CrystalWind.ca!
Articles: Alchemy
Articles: Ancient Egypt
Articles: Labyrinths
Articles: Pyramids
Articles: Superstitions
Follow Us!
Featured This Month
Virgo Mythology
The Virgo Myth In all of constellation mythology, few legends are as misund... Read more
Watermelon Tourmaline
Synonym: Rainbow Tourmaline The watermelon tourmaline is a rare variety t... Read more
Mabon in Modern Times: Fresh Takes on the Au…
The Mabon season begins somewhere around the 21st-22nd of September and cont... Read more
Sun in Virgo
An Overview of Sun Sign Characteristics for Virgo Virgo is guided by Mercur... Read more
Peridot: The Healer's Stone
Peridot has been used as a Power Stone for centuries. Peridot fosters emotio... Read more
Mabon Magic: Ideas For Fall Decoration And R…
Welcome (almost!) to Fall! We’re turning the Great Wheel once again, toward ... Read more
Crystals for Virgo
As the warmth of summer begins to soften into the crispness of autumn, the Sun... Read more
Sweet Violet
Sweet Violet Faithfulness and modesty. “I will always be true to you.” Helps... Read more
The Vine: September 2nd - September 29th
The Autumnal Equinox ( Alban Elfed ) Celtic Symbol : The White Swan Read more